The international situation after World War II was characterized by a strengthening of positions Soviet Union. The sphere of Soviet influence included Finland, Poland, Czechoslovakia, Romania, Bulgaria, Hungary, Yugoslavia, and Albania.
Of the six great states Western world Only two retained their position - Great Britain (although it survived the collapse of the colonial system) and the USA.
People's democratic revolutions are taking place in central and eastern Europe during which, with the support of the USSR, communist parties come to power. During the first three or four post-war years, the bloc of communist states of Eastern and South Eastern Europe. A world socialist system is emerging.
In 1949 The Chinese communists won the decades-long civil war and proclaimed the creation of the People's Republic of China. A huge centralized Chinese state appeared on the borders of the USSR with a population exceeding the population of the USSR by more than three times.
The task associated with consolidating the victory over racism is being consistently solved. In the first post-war years, preparations were underway for peaceful conversations with former allies Germany. Final approval of texts peace treaties were implemented at the Paris Peace Conference (July-October 1946). 21 states participated. The main problem that was considered at this conference was the eradication of fascism, to prevent the revival of fascism. The treaty included articles prohibiting the activities of fascist organizations. Peace talks established post-war territorial changes. A number of articles of peace treaties established restrictions on the armed forces of the defeated states and obliged them to partially compensate for the damage caused to the economies of the victorious parties.
March 5, 1946 Former Prime Minister Churchill gave a speech in American city Fulton with a call to unite the English-speaking states, which symbolized the beginning of “ cold war" A frantic arms race has begun in the world, because... each side (socialism, capitalism) wanted to ensure its military advantage. The Soviet Union mobilized enormous funds to create the atomic bomb and quickly caught up with the United States in this. The arms race and political confrontation on all issues between the two opposing systems created an extremely tense and dangerous situation threatening military conflicts.
In April 1949 The North Atlantic Alliance (NATO) was created - a military-political bloc that included the USA, England, France, Italy, Canada, Belgium, Holland, Portugal and other states. Western Europe.
The entire policy of NATO was aimed at undermining the growing influence of socialist countries and expanding the dominance of the United States and Western countries in the world. The creation of this bloc significantly complicated the international situation and contributed to the intensification of the Cold War.
In the post-war period, the German question remained one of the most pressing issues in international politics. The Soviet Union consistently implemented the program of three “Ds”: demilitarization, democratization, denazification.
Western countries refuse to implement the agreed solution to the German problem. In the western zones of Germany, the three D program was not implemented. In violation of their obligations, the United States and England concluded on December 2, 1946. agreement on the unification of their occupation zones. This led to the split of the German state, and on September 7, 1949. The proclamation of the Federal Republic of Germany took place. In May 1952 An agreement was signed on the creation of the European Defense Community with the participation of Germany and Western states, which meant the creation of its own army in Germany and its inclusion in the “European army”. This step meant the demilitarization of West Germany.
After the Second World War, the collapse of the colonial system began. The United States began to penetrate into regions that before the war were under the control of England, France and other states. Intense rivalry developed in the Near and Middle East. Rivalry between Israel and Arab countries is intensifying.
In 1947 At the session of the UN General Assembly, it was decided to create two states in Palestine - Arab and Jewish. 05/14/1948 part of Palestine was declared the Jewish state of Israel. Soon a conflict arises between Israel and the Arab states. During military operations, Israel seizes part of the Arab territory of Palestine.
One of the results of the Second World War was the liberation of Korea from Japanese occupation. The Soviet Union withdrew in 1945. Its troops are from North Korea, where the Democratic People's Republic of Korea was formed. South of the 38th parallel (according to the agreement between the USA and the USSR, the borders of military operations in the Far East ran along the 38th parallel), the Republic of Korea was proclaimed with a pro-American
government. On the 38th parallel there were continuous armed clashes that resulted in a war between North and South.
The UN, which began its work in January 1946, becomes the military platform for the struggle for peace and international security after the war.
After the war, an organized peace movement emerged and developed. The peace movement covered all continents and countries of the globe.
Thus, the arrangement political forces in the world was characterized by confrontation between two systems (socialism and capitalism), regional conflicts, and the creation of a mechanism for resolving hotbeds of tension.
Topic 1.1 Post-war peace settlement in Europe
Goals: Give an idea of the post-war structure of the world.
Plan
1. Interests of the USSR, USA, Great Britain and France in Europe and the world after the war. Development of a coordinated policy of the Allied powers in Germany.
The USA and the USSR created their spheres of influence, securing them with military-political blocs - NATO and the Warsaw Department. Although the United States and the USSR never entered into direct military confrontation, their competition for influence often led to the outbreak of local armed conflicts around the world.
Churchill in March 1946 in Fulton, USA, made a speech regarding the USSR, and stated that relations between the USSR on the one hand and the USA and Great Britain on the other hand should be built on the military superiority of English-speaking countries. Churchill first of all decided to strengthen relations with the United States, since they had a monopoly on nuclear weapons. This statement exacerbated the confrontation between the USSR and the West
In 1949, the military-political NATO bloc was formed, which included the United States and most countries of Western Europe.
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization, NATO, the North Atlantic Alliance is the world's largest military-political bloc, uniting most European countries, the USA and Canada. Founded on April 4, 1949 in the USA. One of NATO's declared goals is to provide deterrence or protection against any form of aggression against the territory of any NATO member state.
NATO goals:
· act as the basis for stability in the Euro-Atlantic region;
· serve as a forum for consultations on security issues;
· to deter and protect against any threat of aggression against any member states NATO;
· contribute to effective conflict prevention and actively participate in crisis management;
· promote the development of comprehensive partnerships, cooperation and dialogue with other countries in the Euro-Atlantic region.
The northern coalition included: North Korea and her armed forces; Chinese army; The USSR, which also did not officially participate in the war, but largely took over its financing, and also sent air force units and numerous military advisers and specialists to the Korean Peninsula
From the South, South Korea, the USA, Great Britain and a number of other countries took part in the war. peacekeeping forces UN.
Consequences of the war.
The Korean War was the first armed conflict during the Cold War and was the prototype of many subsequent conflicts. She created a model local war when two superpowers are at war limited area without application nuclear weapons. The Korean War added fuel to the fire of the Cold War, which at that time was more associated with confrontation between the USSR and some European countries.
1. "Cold War" is:
1) The system of repression created in the USSR during the years of Stalinism
2) One of the military operations during the Second World War
3) The system of relations established by socialist and capitalist countries after the second world war
4) An attempt by the Western powers to isolate our country after the Brest-Litovsk Treaty
2.The Cold War period refers to the years:
3. The UN was created:
4. Who from American presidents began the “policy of containment” of the USSR?
1) Herbert Hoover
2) Franklin Roosevelt
3) Harry Truman
4) Dwight Eisenhower
5. In 1945, only the following had atomic weapons:
3) France
4) Germany.
6. System international relations, characterized by a balance of approximately equal forces between the competing great powers, was called:
1) monopolar;
2) global;
3) bipolar;
4) international
7. The Truman Doctrine, announced in 1947, boiled down to:
A. the creation of a military-political alliance of Western countries under the auspices of the United States
B. cessation of the production of nuclear weapons
B. the creation of military bases near the borders of the USSR
D. strengthening friendly relations with the USSR
D. support internal opposition in European countries
E. refusal economic relations with socialist countries
8. Effective help North Korea in the Korean War () had:
2) USSR and China
3) China and Hungary
4) Poland and the USSR.
9. In what year did the UN troops land in Korea?
Questions and tasks:
1. Define the Cold War
2. State the main goals of NATO.
3. What were the consequences of the Cold War?
Used Books:
1. History. ( Tutorial for colleges), etc. 2007.
2. http://ru. wikipedia. org
Topic 1.3. Third World countries: the collapse of colonialism and
fight against backwardness.
Goals: Find out the reasons for the collapse of the colonial system
Plan:
1. The growth of the anti-colonial movement.
2. Formation of new independent states as a result of the collapse colonial empires. The influence of the Cold War on liberation movements.
3. Difficulties in overcoming backwardness.
One of the distinguishing featuresXX century- the elimination of the colonial system and the emergence of dozens of new independent states.
The creation of new states on the site of former colonies is the result of the victory of national liberation movements, which were peaceful in a number of countries. Their main achievement was the transition state power from the hands of the device colonial powers in your hands national forces former colonies.
Accelerating the collapse of colonialism in post-war years A number of factors contributed:
1. Extreme aggravation of contradictions between colonies and metropolises;
2. The growing international influence of the successes of socialist construction in the USSR;
3. The balance of forces on the world stage is changing in favor of socialism;
4. The weakening of the position of capitalism as a result of the Second World War
5. Deepening of its general crisis.
6. Education, formation and successful development of the world system;
The crisis of the colonial system began after the First World War.
Already in in several Asian countries and Arab East(Indonesia, India, Iran, Iraq, etc.) there were powerful popular uprisings.
In most colonies the leadership liberation movement The national bourgeoisie, and sometimes a small intelligentsia, took control, creating their own political organizations that led the struggle for political independence. In India still in 1885. National Congress Party was formed in Indonesia in 1927 The National Party arose in Tunisia in 1934 a left-wing nationalist party was created New Dustur.
Victory of the Soviet Union in World War II:
Influenced the search for ways to develop third world countries,
And the search for models of their post-war structure.
China has already 1957 moves away from pro-Soviet politics and independently strives for hegemony over the third world.
In the 70s, the Communist Party of Vietnam began to gradually switch to Chinese positions, and with the collapse of the Soviet Union in economic sphere The “Chinese model of socialism” was established in the country.
Mongolia has started construction Soviet model V post-war period and in 1962 joined the Council for Mutual Economic Assistance, an international economic organization socialist countries under the leadership of the USSR.
Second stage became the final one in political collapse colonialism.
Belgium granted independence to the Congo (Zaire), although mass riots, developed into civil war, slowed down the process of granting independence. The tragedy of Congo (Zaire) did not stop the process of liberation in Africa.
In March 1960 England granted independence to the largest country by population on the continent - Nigeria.
In March 1962, France had to end the war in Algeria and recognize its independence. After the overthrow of the totalitarian dictatorship in Portugal, its colonies - Mozambique and Angola - became independent.
In the 1960s alone, 44 former colonial possessions gained independence. With the liquidation of the Portuguese colonies in 1975, the colonial system completely collapsed. The post-colonial development of the Third World countries began.
Leaving the colonies, the former metropolitan countries sought to maintain their influence there to one degree or another.
Western countries are beginning to use more disguised methods of exploiting newly liberated countries.
Appear various shapes neocolonialism.
At the second stage of the collapse of the colonial system, a restructuring of international relations between the capitalist world and the liberated countries began.
Creation in 1957, according to the Treaties of Rome, of the European Economic Community (now the EU) and the accession of all the colonial possessions of the EEC member countries to it as associated states reflected the West’s desire to use collective forms and methods of neocolonial policy.
In 1958, permanent bodies of the Afro-Asian solidarity movement were created. The final organizational movement occurred in April 1960 at a conference in Xnakri (Guinea), when the charter was adopted and the main goals of this movement were formulated, one of which was to accelerate the liberation of peoples and ensure their economic, social and cultural development. The growth of solidarity among the peoples of the Afro-Asian continent became one of the reasons for the elimination of colonial possessions in Asia and African continent and ensured the transition of the collapse of the colonial system into its final phase. However, later, with the elimination of colonialism, the role of the Afro-Asian solidarity movement constantly decreased.
Thus, the rise of the national liberation movement during the Second World War, the favorable international conditions that arose after the defeat of fascism, led to the collapse of the colonial system of imperialism in its classical forms. The anti-imperialist struggle of the peoples liberated from colonialism is an important force, which, together with the world socialist community, the international workers and communist movement makes a great contribution to the revolutionary renewal of the planet.
Questions and tasks:
1. State the main factors that contributed to the acceleration of the collapse of colonialism?
2. What are the main forms of neocolonialism?
3. What is the main distinguishing feature XX century.
Used Books:
2. The World History. Textbook for universities. , (2009)
3. http://ru. wikipedia. org
Topic 1.4 Dictatorial regimes in the Muslim East
Goals: To form an idea of dictatorial regimes in the East.
Plan:
1.When and why they began to take shape dictatorial regimes? Why are they aggressive?
2. Why Islam was the basis of dictatorial regimes.
3. In which countries did such regimes develop?
Dictatorship (lat. dictatura) - form government, in which all the fullness of state power belongs to only one political position- ruler (dictator), ruling party, ruling group persons, a ruling alliance or a ruling social class.
The Egyptian Constitution of 1923 formally declared it independent state And constitutional monarchy. In fact, the regime of British military occupation remained in the country. In 1951, the Egyptian parliament agreed to unilaterally abolish the Anglo-Egyptian Treaty of 1936, which caused the introduction of British troops into the country and deep political crisis. In this situation in 1952, patriotic military organization The “Free Officers” led by Gamal Abdel Nasser committed coup d'etat. The Revolutionary Leadership Council concentrated all power in its hands.
Stages of the liberation revolution in Egypt.
From 1952 to the early 60s. In Egypt, the first stage of the national liberation revolution was carried out, accompanied by the adoption of the law on agrarian reform (1952), the abolition of the old Constitution (1952), the abolition of the monarchy and the adoption of the Republican Constitution (1956). After the nationalization of the company Suez Canal and the subsequent aggression of England, France and Israel (1956), a law was issued on the “Egyptianization” of foreign banks and firms.
In mid-1961, the second stage of the revolution began. During this period, measures were taken to nationalize banks and enterprises, carry out the second agrarian reform, and introduce state planning. Charter adopted in July 1962 national action rejected the capitalist path of development, and the Interim Constitution of 1964 proclaimed Egypt a “socialist democratic republic.”
L. Johnson, who replaced J. Kennedy, who tragically died in November 1963, began to implement social reforms, called the “Great Society” program. Her central link became the “War on Poverty,” aimed at improving the situation of the poorest segments of the US population. According to statistics, in 1964 there were 36.4 million poor people in the country, which amounted to about 20% of the population, that is, people whose real incomes were below the “poverty level”.
From federal programs important place belonged to a preschool program for poor children.
Was introduced health insurance for elderly citizens, and families with incomes below the “poverty line” received the right to preferential conditions medical care through special federal subsidies to states.
The first group is working with materials from Great Britain.
Fill " business card" Great Britain.
1. Determine the position of Great Britain in the world at the beginning of the 20th century. 2. What is the reason for the development of mass democratic movements and what consequences did these movements lead to for the country? 3. How would you evaluate the reforms being carried out in the country? 4. Which ones are the most productive ways Did Great Britain use to retain its numerous colonial possessions? 5. Explain the concepts: dominions, conservatives, liberals, suffragists, pacifists.
The second group is working with materials on Germany.
Fill out the “business card” of Germany:
1. Determine the main reason why Germany was able to come up with the slogan of redistribution of colonies by the beginning of the 20th century. 2. On what main ideas is the theory of “pan-Germanism” based? Think about which sections of the population and for what reasons could support it. 3. Was it possible to combine the interests of Germany in foreign policy with the interests of other states? Why? 4. Explain the concepts: chancellor, Reichstag, Catholic party, social democracy, agrarian party, pan-Germanism.
The third group is working with materials on France.
Fill out the “business card” of France:
1. Why was there a rapid change of governments in France? Explain what are the positive and negative consequences Such a change can be identified for the development of the country. Which consequences do you think will prevail? 2. Why was the return of Alsace and Lorraine one of the most pressing problems for the country? 3. Evaluate those strong moments in the development of France that it could rely on in the war with Germany. Do they seem sufficient to you to achieve victory? Why? 4. Explain the concepts: unitary state, moderate republicans, radical republicans.
The fourth group is working with materials from the USA.
Create a “business card” of the USA:
1. Identify the factors for the rapid development of the United States at the beginning of the 20th century. 2. What role did the state play in regulating economic development? How can one assess the position of the state? 3. What general and special features of US foreign policy can be named? Can the country's foreign policy at the beginning of the 20th century be considered successful? 4. Is it possible to talk about a special, American path of development? 5. Explain the concepts: immigration, “big stick policy,” “dollar diplomacy.”
The fifth group is work with materials on Austria-Hungary.
Create a “calling card” of Austria-Hungary:
1. Explain why the uniqueness of Austria-Hungary arose and what it was. 2. How multinational composition population of the empire influenced its development and what problems did it create for the authorities? 3. Explain the concepts: dualistic monarchy, national oppression.
The sixth group is working with materials on Italy.
Create a “calling card” of Italy:
1. Think about which features - national or general - more determined the development of the country at the beginning of the 20th century. 2. Can the reforms carried out in Italy at the beginning of the 20th century be called radical and why? 3. Suggest how stable royal power and democratic reforms could be combined. 4. Explain the terms: modernization, “Giolitti era”.
4. Changes in the balance of political forces in the world after the Second World War. Beginning of the Cold War
As a result of the Great Patriotic War and the Second World War, the situation in the world radically changed. The countries of Germany and Japan were defeated and temporarily lost their role as great powers, and the positions of England and France were significantly weakened. At the same time, the share of the United States has increased immeasurably. During the war years, their industrial production not only did not decrease, but also increased by 47%. The USA controlled about 80% of the gold reserves of the capitalist world, they accounted for 46% of the world's industrial production.
The war marked the beginning of the collapse of the colonial system. Within a few years, such largest countries like India, Indonesia, Burma, Pakistan, Ceylon, Egypt. Only post-war decade 25 states gained independence.
In seven countries of Central and Eastern Europe, leftist, democratic forces came to power. The new governments created in them were headed by representatives of the communist and workers' parties.
The most important feature of the post-war period were the people's democratic revolutions in Eastern Europe and a number of Asian countries. During the fight against fascism, a united front emerged in these countries democratic forces, in which the communist parties played a leading role. After the overthrow of the fascist and collaborationist governments, governments were created that included representatives of all anti-fascist parties and movements. They carried out a number of democratic reforms. IN economic field A multi-structure economy has emerged - the coexistence of the state, state capitalist, cooperative and private sectors. Politically, a multi-party system was created parliamentary form political power, in the presence of opposition parties, with separation of powers. This was an attempt to transition to socialist transformations with its own in my own way.
There has been a shift to the left in the political spectrum of European countries. The fascists and the right have left the stage - radical parties. The influence of the communists grew sharply. The role of the Soviet Union, a country that made a decisive contribution to the defeat of fascism, has grown immeasurably. None international problem could not be decided without his participation.
After the war, the foundations were laid for the split of the world into two opposing camps, which determined long years all world practice. During the World War, an alliance of great powers was formed - the USSR, the USA, Great Britain and France. Availability common enemy made it possible to overcome disagreements and find compromises. The decisions of the Tehran (1943), Crimean (1945), Potsdam (1945) conferences were of a general democratic nature and could become the basis for a post-war peace settlement. The formation of the UN (1945) was also of great importance, the charter of which reflected the principles of peaceful coexistence, sovereignty and equality of all countries of the world. However, this unique chance of creating lasting peace remained unused for many generations. The Second World War was replaced by the Cold War.
The term “Cold War” itself was coined by US Secretary of State D.F. Dulles. Its essence is a political, economic, ideological confrontation between two systems, balancing on the brink of war.
The beginning of the Cold War is usually dated to W. Churchill’s speech in the American city of Fulton in March 1940, in which he called on the people of the United States to jointly fight against Soviet Russia and its agents - communist parties.
Economic reasons The change in US policy was that the US became immeasurably rich during the war. With the end of the war they were threatened by a crisis of overproduction. At the same time, the economies of European countries were destroyed, their markets were open to American goods, but there was nothing to pay for these goods. The United States was afraid to invest capital in the economies of these countries, since there was a strong influence of leftist forces there, and the situation for investment was unstable.
In contrast to the bloc of Western states, an economic and military-political union of socialist countries began to form. In 1949, the Council for Mutual Economic Assistance was created - a body economic cooperation states of Eastern Europe. It included Albania (until 1961), Bulgaria, Hungary, Poland, Romania, Czechoslovakia, and since 1949 the GDR. The seat of the CMEA Secretariat was Moscow. One of the reasons for the creation of CMEA was the boycott by Western countries of trade relations with the USSR and the states of Eastern Europe.
The confrontation between the parties clearly manifested itself in 1947 in connection with the Marshall Plan put forward by the United States. European countries help was offered to rebuild the devastated economy. Loans were given for the purchase of American goods; the proceeds were not exported, but were invested in the construction of enterprises on the territory of these countries. The Marshall Plan was adopted by 16 Western European countries. Political condition assistance was the removal of communists from governments. In 1947, the communists were removed from the governments of Western European countries. Help was also offered to Eastern European countries. Poland and Czechoslovakia began negotiations, but under pressure from the USSR they refused assistance. At the same time, the United States broke the Soviet-American loan agreement and adopted a law banning exports to the USSR. Soviet government regarded the Marshall Plan as a weapon of anti-Soviet policy.
The ideological justification for the Cold War was the Truman Doctrine, according to which the conflict between Western democracy and communism is irreconcilable. The tasks of the United States are the fight against communism throughout the world, “containing communism,” “throwing back communism within the borders of the USSR.” American responsibility for events taking place throughout the world was proclaimed; all these events were viewed through the prism of confrontation between communism and Western democracy, the USSR and the USA
One of the forms of manifestation of the Cold War was the formation of political and military-political blocs. In 1949, the North Atlantic Alliance (NATO) was created. It included the USA, Canada and several Western European countries. Two years later, a military-political alliance was signed between the United States, Australia and New Zealand.
The Soviet Union worked against propaganda new war. The main arena of his activities was the United Nations (UN). It was created in 1945 and united 51 states. Its goal was to strengthen peace and security and develop cooperation between states. At UN sessions, Soviet representatives made proposals to reduce conventional weapons and ban atomic weapons, on the withdrawal of troops from the territories of foreign states. All these proposals, as a rule, were blocked by US representatives and their allies. The USSR unilaterally withdrew its troops from the territories of several states where they had been deployed during the war years.
In May 1955 - the Warsaw Military-Political Pact. The split of the world into two opposing camps was taking shape. The split of the world into two camps affected economic ties. After the adoption of the Marshall Plan and the formation of CMEA, two parallel world markets actually emerged, with few related friend with a friend. USSR and Eastern Europe found themselves isolated from developed countries, which had a detrimental effect on their economy.
The provision about two camps, about the confrontation on the world stage of two social systems underlay the foreign policy views of the party and state leadership of the USSR. Stalin pursued a tough policy within himself socialist camp, consistently implemented the principle “those who are not with us are against us.” Reprisals against dissidents were carried out within socialist countries. If the leadership of the country took a special position, then this country was excommunicated from the socialist camp, broken with it external relations, as happened in 1948 with Yugoslavia, whose leadership tried to pursue an independent policy.
Actions of the USSR - liquidation of the US nuclear monopoly. Atomic bomb was tested in the USSR in 1949, created in 1953 thermonuclear bomb(earlier than in the USA). The creation of atomic weapons in the USSR was a response to American atomic blackmail, but marked the beginning of an arms race between the USSR and the USA.
US plans: atomic bombing of the USSR, doctrine of containment and rejection of socialism. American historians, without denying the existence of such plans, say that we were talking only about operational military plans that are drawn up in any country in case of war. But after the atomic bombing of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, the presence of such plans could not but cause a sharp response from the Soviet Union, since this atomic bombing wasn't so much military operation, as much as a political act, with the aim of putting pressure on the USSR.
The standard of living of the population. 2.1. Main directions of social policy Soviet leadership in the post-war period. Measures to solve the main problems of society. Most main task V social policy Soviet leadership in the post-war years was to solve all the main problems as much as possible short term. For this purpose March 18, 1946 The Supreme Council The USSR approved the government's...
The final chord was the entry of the Federal Republic of Germany into NATO, and the GDR into the Warsaw Pact Organization. As the divergence increases, yesterday's allies in construction post-war world the attitude of the Soviet leadership to the forms of control over the situation in the countries also changed “ people's democracy" They gradually became elements of the world socialist system. Positions of the USSR in countries...

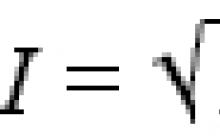








"pros" and "cons" of democracy
Surveyor. Who is a surveyor? Description of the profession. Profession surveyor Surveyor training
Magellanic clouds: who are they?
Pepper Steak Sauce Creamy Pepper Sauce
How to create a competent portfolio for a designer