
Red or mountain wolf It has a body up to 1 meter long, and can weigh from 12 to 21 kg. Outwardly, it can be confused with a fox, and this is precisely one of the main reasons for its extinction. He attracted people's attention with his fluffy fur, which has a beautiful bright red color. Its tail is slightly different from a fox's, having a black tip. The habitat of this wolf is Far East, China and Mongolia.

Amur leopard In Russia, this species, which is on the verge of extinction, can be found in the Primorsky Territory. It is worth noting that in 2013, in southwestern Primorye, experts were able to count 49 Far Eastern leopards based on tracks. This animal is strictly protected in China, where killing it is punishable by the death penalty. The Amur leopard has become a critically endangered species mainly due to poaching.




![]()
For centuries, people took from nature whatever they wanted, sparing nothing and no one, without thinking about the consequences. Because of this, many plants and animals have already disappeared from the face of the earth, and many others are about to disappear. Instead of forests, deserts appeared, and instead of clean rivers, muddy streams flowed, from which you cannot drink, in which you cannot swim. There are fewer and fewer butterflies and dragonflies on forest edges. But there is more and more garbage, fire pits, and broken trees. Every person must understand that nature is in a bad place right now. And I must definitely help her! Like a friend in trouble.


A huge number of flora species grow in the vastness of Russia. These are trees, shrubs, herbs and flowers. Despite the fact that there is a large number of green areas, such as forests, meadows, steppes, in the country a huge number of plant species are on the verge of extinction. These plants are included in the Red Book, they cannot be picked and are under state protection.
Lists rare species floras are updated all the time, but despite this, we can only see an approximate picture, since today there are no methods for accurately establishing the number and distribution area of certain species. Based on their data latest edition Red Book of the Russian Federation, it includes more than 600 plant species. Each species has six statuses indicating its stage of extinction, ranging from declining to probably extinct.
Endangered species of flora
A large number of endangered species grow in the steppe, in Siberia, the Caucasus, and in the coastal zone. The following representatives of the plant world are included in the Red Book of Russia:
Moss moss – Polushnik lake, Polushnika asiatica;
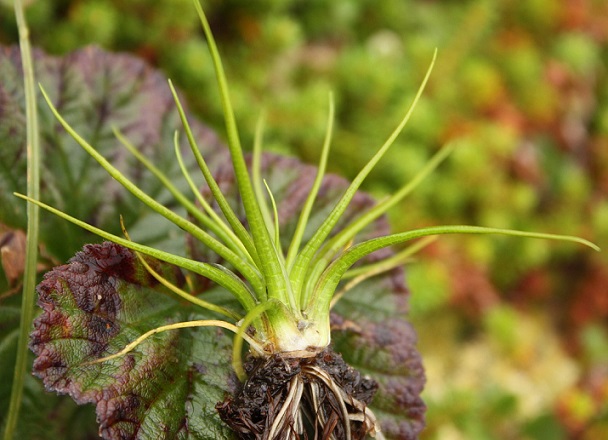

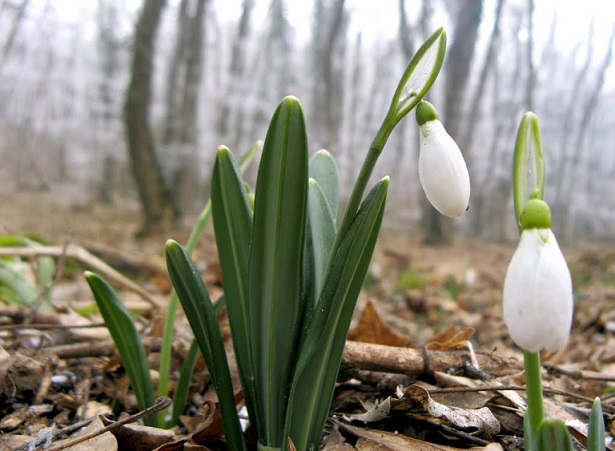
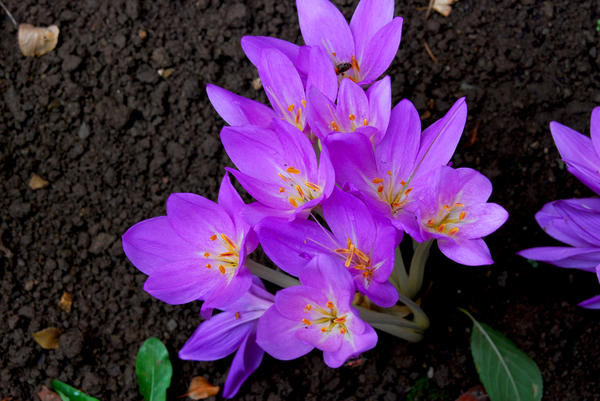
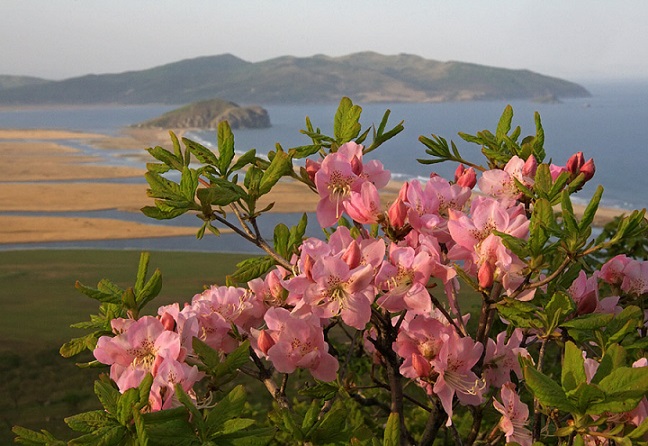
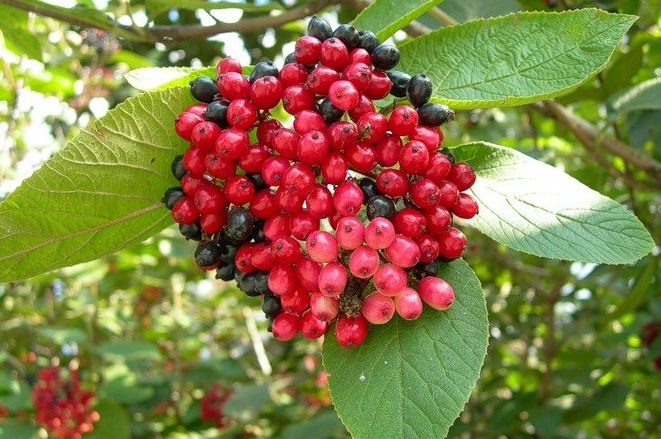
Angiosperms - Snowdrop flat-leaved, Volodushka Martyanova, Colchicum cheerful, Rhododendron Schlippenbach, Dwarf tulip, Magnolia obovate, Common fig, Stephen's stork, Sedge Malysheva, Deytsia smooth, Mongolian nuthopper, Common pomegranate, Petiolate almond, Cinnabar cotoneaster, Orbberry sumacifolia;

![]()








![]()




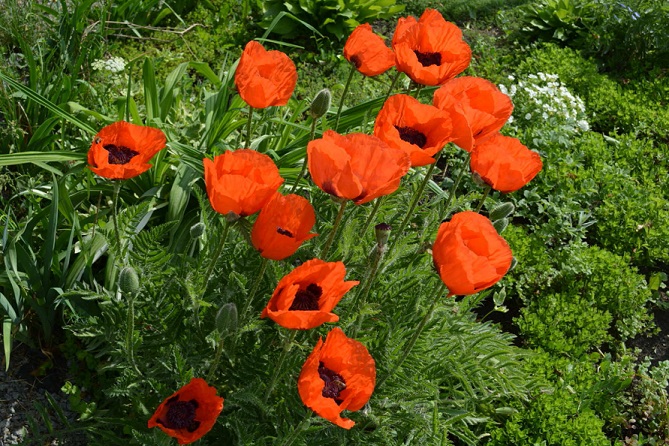
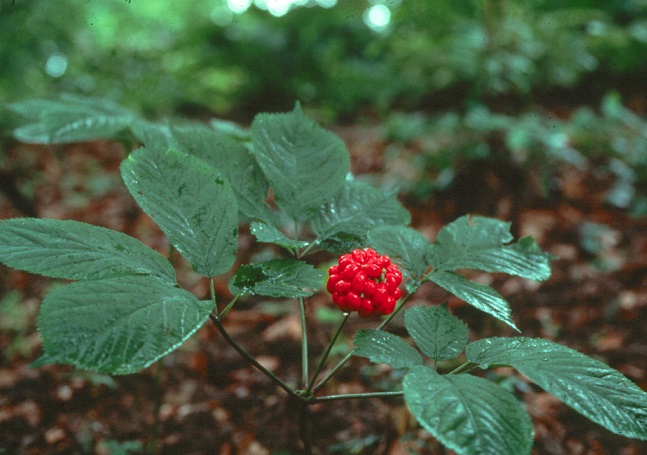
Flowering plants – Nut lotus, Mountain peony, Oriental poppy, Sayan buttercup, Notched violet, Common ginseng;






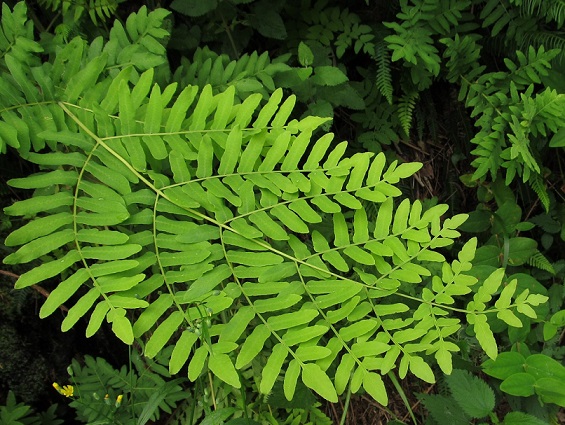
Ferns – Marsilea egyptianum, Common rosewort, Kuna's fringeweed, Claytonov's chistoust, Wright's mecodium;











Lichens – Lobaria pulmonata, Letaria volens, Glossodium japonica, Leptogium Burnet, Parmelia Borisova, Cetraria Komarova, Asahinea Scholandera;


Mosses – Fossombronia Alaskan, Capania globulus, Cryphea multidirectional, Oreas Marcius, Taxiphyllum alternating, Gomaliadelphus smoothtoothed;
Mushrooms – Amanita agaric, Curly sparassis, White boletus, Maiden's umbrella mushroom, Grifola curly, Mutinus canis, Rogatik pistil, Cone mushroom flocopede.


White boletus
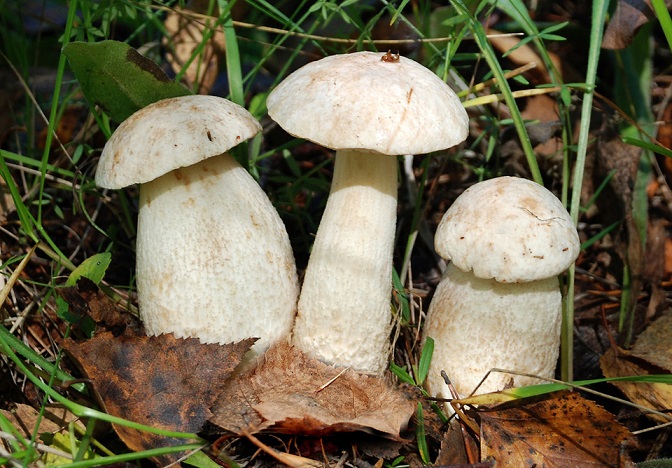
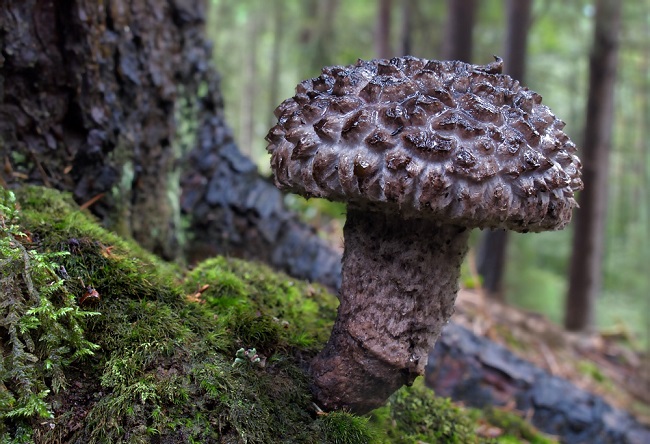



This is far from full list all types of flora that are on the verge of extinction in Russia. The condition of some of them is very critical, and everything is heading towards the fact that many plants will irrevocably disappear from the face of the earth.
Protection of rare plant species
Collecting data and regularly updating the lists of the Red Book of Russia is a small drop of what will help preserve the country’s flora. Species that require special treatment and conservation regularly appear. It is worth emphasizing that in mountainous areas, rare plants are located precisely on the mountain slopes. This ensures some safety. Despite the fact that the mountains are regularly conquered by climbers, this flora has a chance of being preserved. In addition, in some areas, rare plants are found in places where human activity is not so active and industrial development does not threaten the plant world.
In other regions, where endangered species grow in fields and within cities, the plants must be jealously protected. This is how we need to fight deforestation and poaching. Besides, in last decades the territory is actively shrinking protected areas and wild natural objects. Not least important is the pollution of the atmosphere, lithosphere, and hydrosphere, which also negatively affects the world of flora. However, the safety of plants mainly depends on the entire population of our country. If we take care of nature, we will be able to preserve rare and valuable plant species.
It seems that with the appearance on the shelves of pharmacies in 1998 of drugs that could completely cure erectile dysfunction, people had to stop using rare plants and animals for sexual purposes. Unfortunately, this did not happen, mainly due to local cultural traditions and the high cost of such drugs. Men have sought a cure for sexual dysfunction for thousands of years by eating various animals or their individual organs. Because of this, we have brought to the brink of extinction (or have already destroyed) some individual species plants and animals.
10. Wiggle (aka jack or bustard)
This rare bird was nearly hunted to extinction throughout the Arabian Peninsula due to speculation that its meat was an aphrodisiac. Currently, this bird is listed in the Red Book as “endangered”, but it is still hunted by those who want to satisfy their urges by eating the meat of this bird.
In Pakistan, hunting for wigglers is prohibited, but this does not prevent members of the Arab royal family organize annual hunts for these chicken-sized birds. Pakistan quietly issues 25-35 special permits a year to wealthy sheikhs, which allow them to hunt birds in their wintering grounds. This hunt is quite controversial, with most participants well exceeding the 1,000 bird limit, which threatens the species' extinction.
9. Silphium

When we think of birth control in the 21st century, we usually think of condoms, the pill, and all sorts of devices. But long before all these things were invented, people used a plant called silphium. Silphium was collected by our ancient ancestors for its contraceptive effect when taken orally.
The ancient Greeks and Romans used silphium for over 700 years until it finally died out in the first century BC. Planting silphium so depleted the soil that it was no longer able to support further plant breeding. Silphium became extinct due to the hyperactive sexuality of our ancestors, who did not want to have... us.
8. Yarsagumba insect mushroom - “Himalayan Viagra”

Yarsagumba is a Nepalese mushroom that has been used for centuries as an aphrodisiac. It sells for $25-$150 per gram, with the price rising as supplies dwindle. Due to excessive demand, the mushroom is in danger of extinction, and this could happen as early as soon. Unlike others on this list, it is used not only to treat erectile dysfunction in men, but also to enhance libido in both men and women.
The mushroom is so popular among residents South-East Asia, that its global sales are $5-11 billion per year. Demand kills the mushroom because it is harvested before it reaches sexual maturity, the point at which the mushroom spreads its spores. This prevents new spores from entering the soil and makes its extinction almost certain.
7. Black rhinoceros

Rhino horn has been used in Chinese medicine for more than 1,800 years, but a recent surge of interest in it in Vietnam has brought the black rhinoceros to the brink of extinction. There is an opinion that it can cure cancer, eliminate liver problems, and much more. Currently, in Vietnam, rhino horn has become more valuable than gold, its price reaches $100,000 per kilogram. Doctors prescribe it to members of Vietnam's wealthy elite, and increased demand has significantly reduced the species' population.
The idea that the horn is used as an aphrodisiac is a Western myth, but the myth has been so widespread over the years that the demand for rhino horn has skyrocketed in Vietnam. Rhinoceros horn contains only keratin and has no recognized medicinal properties, but this does not stop those who want to increase their potency. Currently, black rhinoceroses are listed in the Red Book as endangered.
6. Oysters
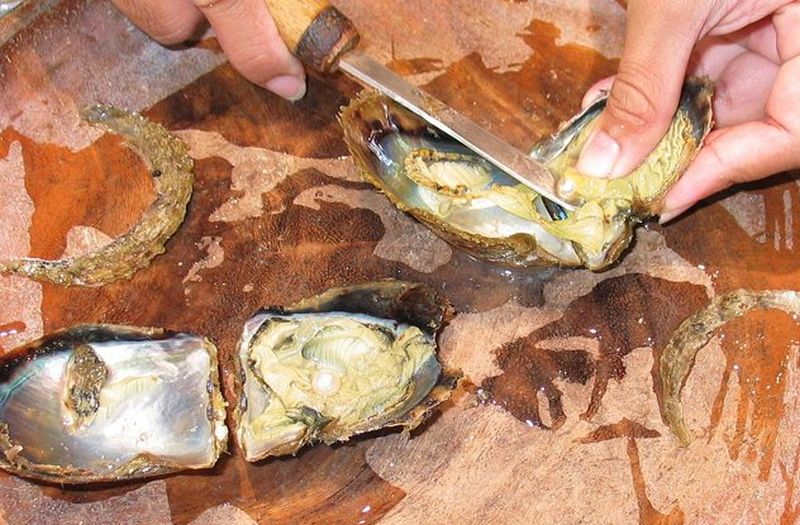

Oysters have long been considered an aphrodisiac in numerous cultures around the world, which is why wildlife they are becoming increasingly rare. In many parts of the world's oceans, wild oysters have already become extinct due to overfishing, disease and mass harvesting.
The loss of wild oysters around the world is a serious problem for several reasons. Oysters are very effective nitrogen filters and remove dangerous contaminants from water - each oyster “filters” almost 200 liters of water per day. Whether you eat them to enhance your sexual performance or simply because you like their taste, you should know that one day they may become a thing of the past.
5. “Sex tree” citropsis

Some men in Uganda are increasingly fearful for the fate of the Citropsis tree, which locals more commonly call the "omumboro" or "sex tree." Citropsis roots are used to combat erectile dysfunction, and its potential extinction is a major concern. Men interested in root swallowing tend to uproot the tree and make no attempt to replant it, which has led to an overall decline in the number of these plants.
Scientific research into the effectiveness of Citropsis has led to interesting discovery. During experiments with male rats, testosterone levels and the number of sexual contacts significantly increased in the experimental subjects. The plant contains Chemical substance, which affects the vascular system, which is why it appears to be effective for men.
4. Tigers
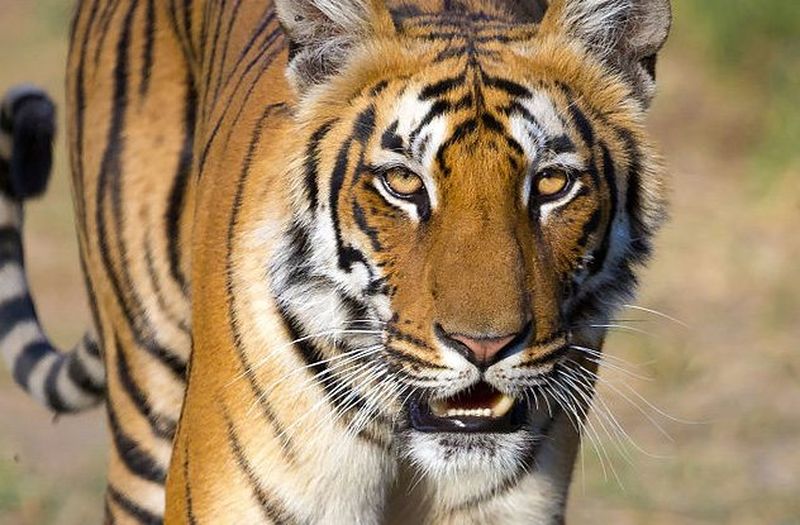

Sometimes an animal is chosen as a healing object for men simply because it is considered incredibly masculine in its own right. Tigers have long attracted the attention of Eastern medicine for their aggressiveness. Everyone who has encountered them assumes that a tiger can easily kill even the largest and strong man on the planet (and they are 100 percent right).
Tigers have been a part of traditional Chinese medicine for thousands of years. Doctors use almost every organ of theirs - from their eyes, whiskers, and brains to their blood, flesh and penis. To combat male impotence and decreased libido, crushed tiger bones are used. Due to the fact that tigers are already very long time attract the attention of hunters, they are endangered. Some subspecies, such as the Balinese, Caspian and Jamaican tigers, are already extinct.
3. Sperm whales

These giant mammals attract attention because of what is produced in their guts. The digestive tract of sperm whales produces a substance called ambergris. It has long been used by many peoples to treat sexual dysfunction in both men and women. The peculiarity of this particular aphrodisiac is that there is scientific evidence of its real influence- even when the man receiving it does not have a female partner.
Scientists conducted experiments on male rats to determine the degree of their excitability in the absence of females. Yes, a group of male rats was given a doll to observe their behavior. And they did it. The study concluded that “the present results... support the feasibility of this folk remedy as an aphrodisiac." Unfortunately, the International Union for Conservation of Nature and natural resources recognized sperm whales, like many other whale species, as endangered.
2. Pangolins
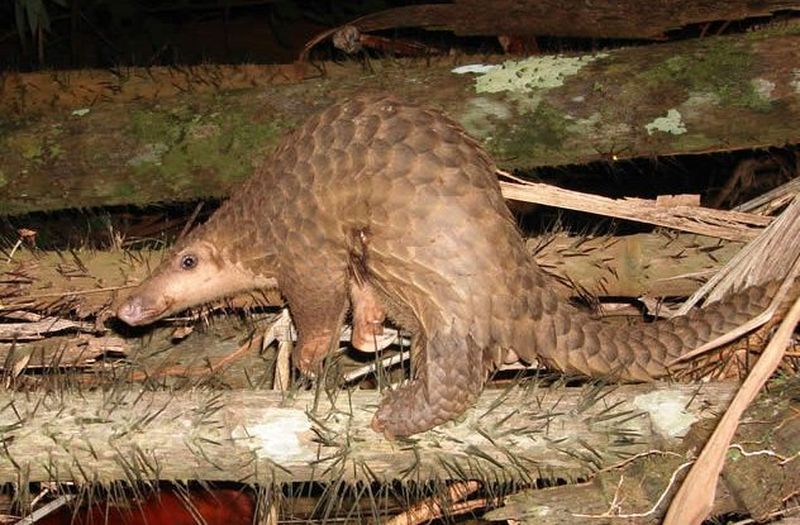

If you've never seen a pangolin, even at your local zoo, all you need to know is that they are an adorable cross between a small anteater and an armadillo. For some reason, for centuries, people have believed that the armored anteater is good for male libido. Because of this, pangolins are the most commonly sighted animal in the world. illegal trade animals.
Pangolins are native to Cambodia, Malaysia and Indonesia, but the market for thousands of frozen small animals has become ships bound for China. Pangolin meat has long been considered an aphrodisiac, and there are several ways to prepare and consume it; scales are considered a means of treating anything - from inflammation of the lymph nodes to lack of production breast milk among women. Pangolins are currently listed as critically endangered and it is likely that if the trade continues at current levels, pangolins will become extinct before the end of the century.
1. Water frog scrotum
![]()
Imagine you are walking and notice something that can only be described as a frog shaped like a scrotum. Okay, now pick it up and eat it. Sounds pretty nasty, doesn't it? But someone once did, and now the animal is dangerously close to extinction.
In fairness, it must be said that this animal is officially called the “Titicaca water frog”, or “Titicaca whistler”, it lives in Lake Titicaca in South America. But it is often called the scrotum frog due to the abundance of folds in the skin that make the animal look like... well, you get the idea. This species is nearing extinction and has been listed as critically endangered, due in large part to their capture for use as an aphrodisiac.
People like to consume the meat of this frog in the form of puree by grinding it and mixing it with honey, roots of local plants and some other local products. It is believed that this puree creates a mood conducive to fun and games, but there is no scientific evidence, confirming this. Despite this, the frog in the form of a male rattle may disappear forever due to man's endless need to satiate his desire.
Although we rarely talk about them, there are several plant species with their own unique characteristics that are limited in number and habitat.
As with animals, the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) has classified each of these species as “critically endangered.” Faced with extinction, rare plants are now extremely vulnerable, and efforts to conserve them are as necessary as those to save or African plants. This article provides a list and a brief description of the rarest plant species on Earth.
Nepenthes Attenborough
Unique plant Nepenthes Attenborough ( Nepenthes attenboroughii), named after the famous naturalist Sir David Attenborough, was discovered back in 2007 in the Philippines. It is endemic to the slopes of Mount Victoria on the island of Palawan, Philippines. Nepenthes Attenborough's limited habitat has made it vulnerable to extinction. The plant is characterized by bell-shaped pitchers that some experts say are large enough to lure rats inside.
Suicide Palm

Another species of rare plants in the world, discovered in 2007, is the suicide palm ( Tahina spectabilis). The plant is endemic to the Analalawa region of Madagascar and is also classified as a "Critically Threatened Species" according to the IUCN. The suicide palm got its name because of its inherent feature. At about 50 years of age, the palm tree experiences a sudden burst of inflorescences at the top, affecting the plant so much that immediately after this event the tree withers and dies. The palm typically grows up to 5 m in height and has a crown diameter of about 18 m.
Risantella Gardner

Risantella Gardner ( Rhizanthella gardneri) is a rare plant species that is endemic to Western Australia. This is the only type of orchid that throughout life cycle grows underground. Large scale cleanup to maintain Agriculture is the main threat to this unique orchid species.
Echinomastus mariposensis
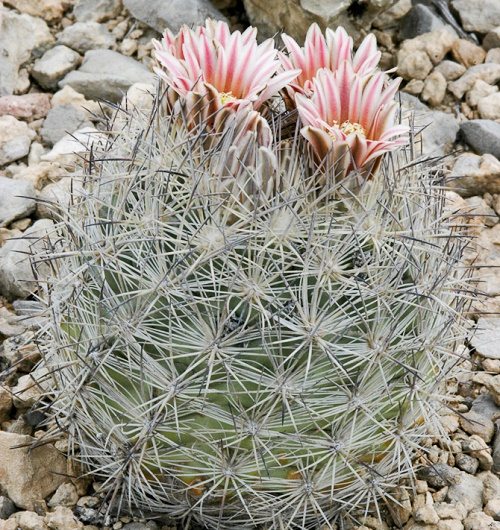

This type of cactus is also called "golf ball" because of its ball-like shape and the white spines surrounding the plant. It is endemic to a small area between Booster County, Texas, USA, and Coahuila, Mexico. The rarity of the plant and its limited range led to the classification Echinomastus mariposensis, as a critically endangered species in the United States. Over the past 20 years, almost 95% of the population has been lost due to illegal harvesting, which is one of the main causes of extinction.
Encephalartos hirsutus
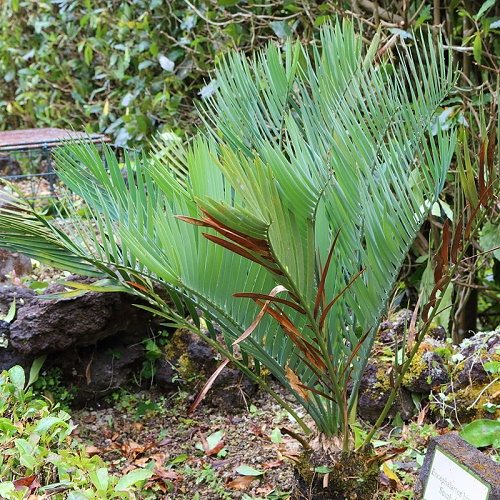

One more important look plants that deserve direct attention from environmental organizations is Encephalartos hirsutus. This plant is endemic to the Limpopo province in South Africa, and currently only a few representatives of this species remain. Some even argue that the species is already extinct, although the IUCN classifies it as critically endangered. The use of this plant for decorative purposes is considered the main cause of extinction.
Medusagina

Medusagina ( Medusagyne oppositifolia) got its name because of the fruits that appearance resemble jellyfish. The plant is endemic to the island of Mahe in the Seychelles archipelago. Medusagina was rediscovered in the 1970s, and the species is now critically endangered with only about 86 mature individual plants growing in the wild.
Acacia anegadensis

Acacia anegadensis distinguished by extremely sharp spines. The species, endemic to the British Virgin Islands, could soon become extinct as rising sea levels threaten to wash away these low-growing shrubs. However Acacia anegadensis can be found in the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, England, thanks to which the species will survive even if it disappears in the wild.
Anogramma ascensionis

This plant is very similar to ordinary parsley, growing on a tiny, volcanic island Ascension in the southern part Atlantic Ocean. The plant was thought to have gone extinct more than half a century ago, but a team of botanists studying plants on the island rediscovered the species in 2009. Scientists estimate that only 40 mature plants of this species are found in the wild today, necessitating the classification of the plant as critically endangered.
Erythrina schliebenii

Erythrina schliebenii- A critically endangered species of coral tree, it was thought to be extinct in 2008 when the vast forest areas in which these trees grew were destroyed. However, in 2012, a small population of 50 trees was discovered in a small area in Tanzania, and this is currently the last known population Erythrina schliebenii in the world.









"pros" and "cons" of democracy
Surveyor. Who is a surveyor? Description of the profession. Profession surveyor Surveyor training
Magellanic clouds: who are they?
Pepper Steak Sauce Creamy Pepper Sauce
How to create a competent portfolio for a designer